It's clear that the buildings we live and work in each day stand as silent sentinels to our quality of life. Yet, they also echo the environmental footprint we leave behind.
Building codes, the DNA of our infrastructure, have long laid the groundwork for safety and design standards. However, as the drumbeat for environmental sustainability grows louder, there's an emerging narrative — the need to weave sustainability into the very fabric of these codes.
Take a moment to consider how sustainable practices could reshape the spaces around you. Incorporating advanced technologies like ThermoDrain into building codes is not just a leap forward; it’s a necessary stride towards a future where our homes and businesses harmonize with the environment.
With this in mind, we're not just building structures; we're nurturing ecosystems.
Understanding ThermoDrain Technology
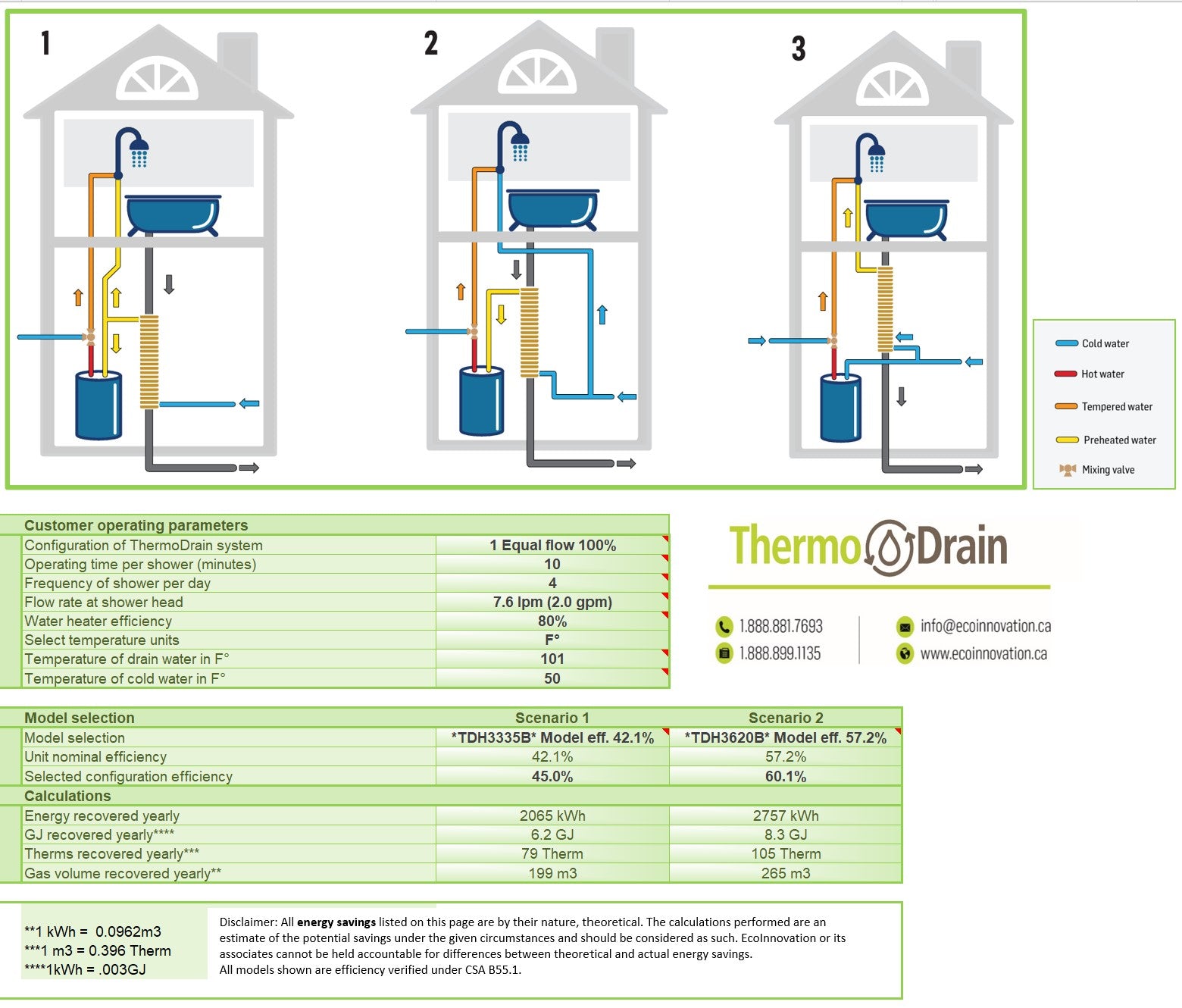
Peek beneath the surface of ThermoDrain technology, and you'll find a seamless blend of simplicity and innovation - a system that not only captures warmth from wastewater but also has the potential to reduce hot water heating costs by up to 30%. Its design allows it to reclaim a significant amount of heat—up to 60% of the energy that would otherwise be lost. This substantial energy recapture underscores ThermoDrain's compatibility with the goals of contemporary municipal building codes, which increasingly emphasize sustainability alongside safety and comfort.
As mentioned - it’s a system designed to capture the warmth from wastewater — think showers, dishwashers, and washing machines — and use it to preheat incoming cold water. This recovered heat means your water heater does less heavy lifting, and as a result, consumes less energy.
The elegance of ThermoDrain lies in its universal application. It’s a technology ready to work with existing infrastructures, making it an ideal candidate for integration into municipal building codes. It’s not about reinventing the wheel; it’s about enhancing the rotation with smarter, sustainable efficiency.
By understanding the mechanics and benefits of ThermoDrain, we lay the foundation for smarter building practices. It's a system that epitomizes modern sustainability — ready to be embraced by building codes that prioritize the future without compromising on the comforts of today.
The Role of Municipal Building Codes in Environmental Stewardship
Municipal building codes serve as the architects of our communities, shaping the standards to which our homes and offices are constructed and renovated. Beyond their traditional focus on safety and accessibility, these codes are now assuming a vital role in environmental stewardship. With each revision, there is an opportunity to embed sustainability deeper into the urban fabric, setting the stage for future generations to inhabit a cleaner, greener world.
The integration of technologies like ThermoDrain into these codes is not just an enhancement; it's a transformation.
Municipalities that pioneer this integration are not simply adopting new tools; they are championing a vision. They understand that the decisions made today about how buildings are designed and retrofitted have direct implications on the community’s carbon footprint and resilience in the face of environmental challenges.
As local governments re-evaluate building codes, the inclusion of ThermoDrain stands out as a strong stride towards reducing energy consumption. This technology, with its potential to lower greenhouse gas emissions and bolster energy efficiency, can become a pillar of municipal climate action plans. By embracing such innovations, community leaders can ensure they are not only upholding current standards of sustainability but are also crafting a legacy of ecological foresight.
Regulatory Landscape and Comparative Analysis
In Canada, building codes and sustainability are tightly integrated, with federal, provincial, and territorial governments collaborating to set rigorous standards aimed at reducing energy consumption and promoting green building technologies.
The National Building Code of Canada (NBC) and provincial variations, such as the Ontario Building Code (OBC) or British Columbia Building Code (BCBC), mandate energy efficiency measures and increasingly emphasize the use of renewable energy sources and energy recovery systems.
Similarly, in the United States, building regulations vary by state, with national standards like the International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) providing a baseline for energy efficiency. States like California have adopted stringent measures such as Title 24, which require new buildings to meet strict energy efficiency standards and promote the use of technologies like solar power and heat recovery systems.
ThermoDrain's integration into building codes differs slightly between Canada and the US due to these regulatory nuances.
In Canada, where building codes often mandate specific energy efficiency targets and renewable energy utilization, ThermoDrain fits seamlessly into existing frameworks by enhancing energy recovery and reducing operational costs for homeowners and businesses alike.
Conversely, in the US, adoption of ThermoDrain may vary depending on state-specific incentives and mandates. States with robust energy efficiency programs and incentives for green building technologies are more likely to see widespread adoption of ThermoDrain, whereas others may require additional advocacy and education to demonstrate its benefits and feasibility.
ThermoDrain and Energy Efficiency: A Closer Look
The conversation around energy efficiency often circles back to one key question: How can we do more with less? With its ability to reclaim heat from wastewater, ThermoDrain offers a compelling answer, and has the case studies to prove it.
This system is a testament to efficiency, a beacon of conservation in a world striving to cut energy use without compromising comfort or convenience. Studies tracking the performance of ThermoDrain have illuminated its ability to reduce energy consumption substantially. In the context of a single-family home, the savings are notable, but when scaled up to multi-unit residences or commercial buildings, the impact is even more significant. This is energy efficiency in action — measurable, meaningful, and ready for mainstream adoption. The case for including ThermoDrain in green building standards becomes increasingly compelling when we consider these quantifiable gains. It's a move that aligns with the broader shift towards energy-efficient building practices, setting a precedent that could reshape industry norms.
By advocating for ThermoDrain's inclusion in building codes, we're not just championing a product, we're fostering an entire ethos of sustainability that resonates with people from all walks of life.
The Economic Benefits of Integrating ThermoDrain
Sustainability is often related to economics, too. It's essential to address the financial viability of integrating green technology like ThermoDrain into building practices. For municipalities and property owners alike, the fiscal aspect of adopting energy-efficient technologies can be a driving factor.
Let's delve into the kind of savings that these stakeholders could realize by incorporating ThermoDrain into their infrastructure.
Cost analysis reveals a compelling narrative: by reducing the load on water heaters, ThermoDrain can significantly decrease energy bills. This isn't just a marginal saving; it's a reduction that can make a tangible difference in operating costs over time. For municipal buildings and public facilities, where budgets are carefully allocated and scrutinized, the inclusion of such technology can lead to more financially sustainable operations.
For residential properties, the savings imparted by ThermoDrain create an attractive selling point for eco-conscious buyers and can increase the market value of a home. The long-term financial incentives for adopting this technology thus extend beyond immediate energy bill reductions to potential property appreciation and marketability. As property owners consider the lifecycle costs of their investments, ThermoDrain stands out as a financially prudent choice.
Collaborative Efforts: Working with Industry Experts
The path to integrating ThermoDrain into municipal building codes is not one to be walked alone. It is a collaborative journey that calls for the expertise and insights of a diverse set of stakeholders. Policymakers, industry experts, and ThermoDrain manufacturers all have a part to play in aligning objectives and ensuring that the inclusion of this technology into building practices is both seamless and effective.
Collaboration starts with open dialogue, where industry leaders can share their knowledge about the ins and outs of ThermoDrain, its installation processes, and maintenance.
Policymakers, in turn, benefit from this dialogue by gaining a deeper understanding of the technology's practical implications, which can inform more nuanced and robust building codes.
These partnerships are vital in crafting policies that are not only aspirational in their commitment to sustainability but also grounded in the realities of construction and building management. By working hand-in-glove with those who design, produce, and install ThermoDrain systems, municipalities can ensure that the codes they develop are not just good on paper but also in practice, fostering a built environment that truly reflects our collective commitment to a sustainable future.
The Path Forward: Steps to Amend Municipal Building Codes
As North America transitions towards a greener future, the amendment of municipal building codes to integrate technologies such as ThermoDrain becomes an actionable and necessary step.
For policymakers looking to update building regulations, a strategic and methodical approach is crucial. It begins with a thorough understanding of the current codes and the gaps where improvements in sustainability could be made.
Building codes are living documents, ever-evolving to meet the changing needs of society. To amend these codes, one must engage in a comprehensive review process that involves stakeholders from various sectors, including construction, environmental science, and technology. Public consultations, expert panel discussions, and pilot projects can provide valuable insights into the practical application and benefits of technologies like ThermoDrain.
As policymakers navigate the legislative process to incorporate ThermoDrain into building codes, they must also consider the training and resources needed for proper implementation. It is about laying the groundwork for smooth adoption, ensuring that when the new codes come into effect, the transition for builders and developers is as clear and straightforward as possible.
Conclusion: Paving the Way for Greener Communities
In shaping communities that promote a sustainable tomorrow, the choices made today are fundamental. The integration of ThermoDrain into municipal building codes is more than just an update to regulations; it is a commitment to a cleaner, more efficient way of living. The imperative for all stakeholders involved becomes clear: to collectively advocate for and support policy changes that reinforce the community’s dedication to sustainability.
Building practices inspired with innovative solutions like ThermoDrain not only contribute to achieving environmental goals but also help to catalyze a broader cultural shift towards green living - for the prosperity of future generations.
The advancement of green technologies in building codes signifies a pivot point for the industry. It calls upon consumers to demand more sustainable homes, developers to construct them, and legislators to support them.

















No comment yet, add your voice below!